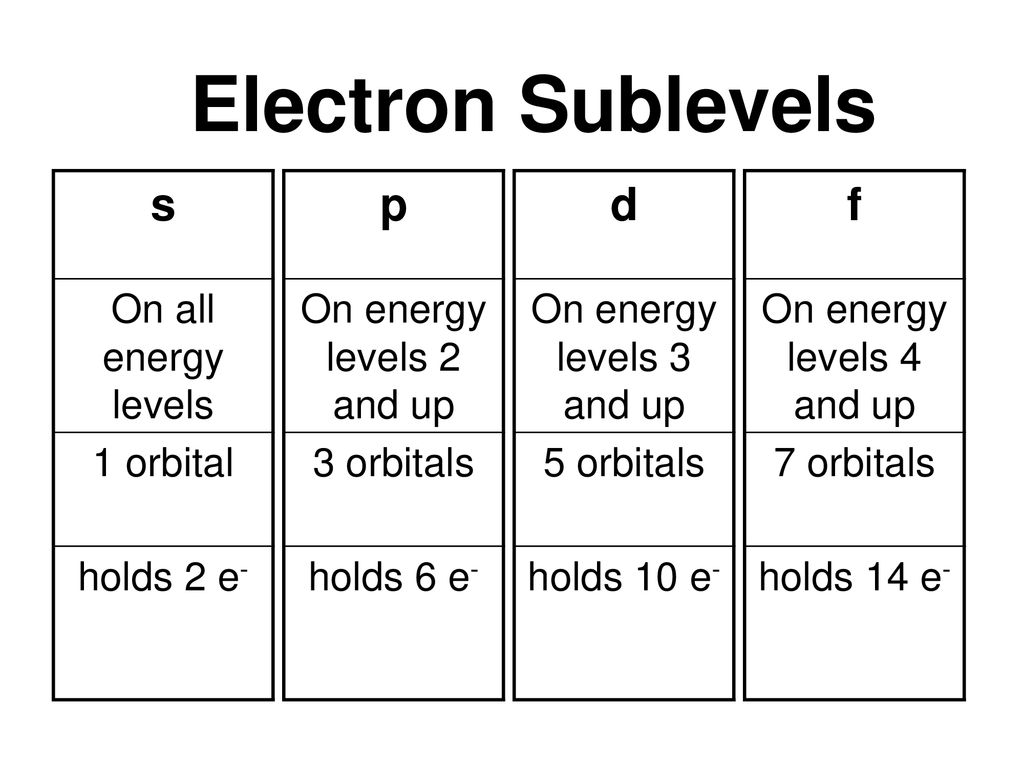
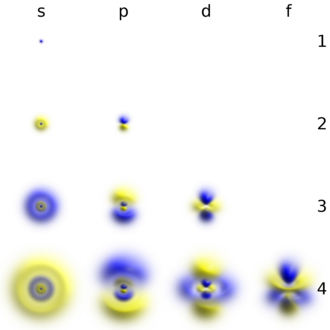
コレクション s p d f orbitals values 127554-What are s p d f orbitals
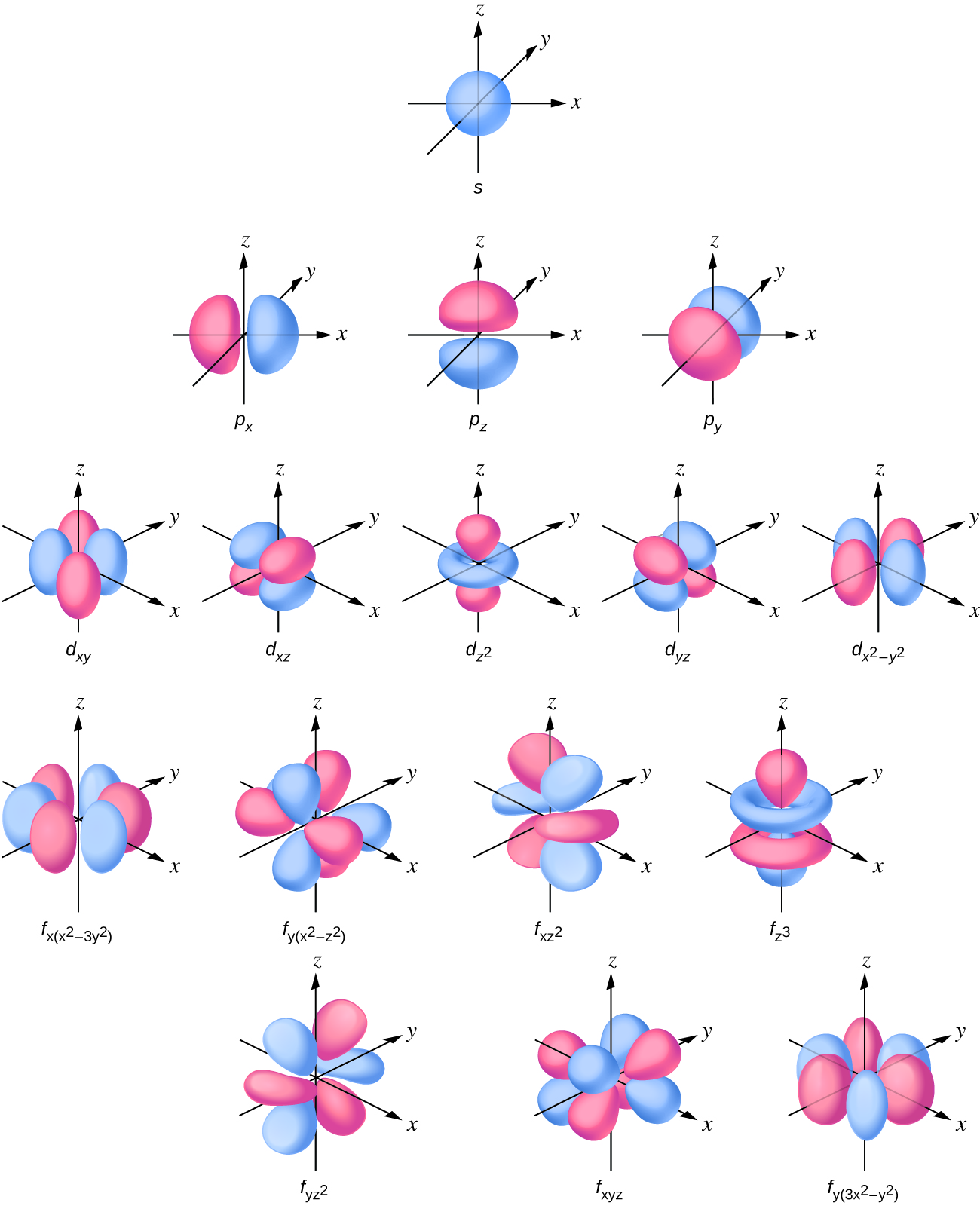
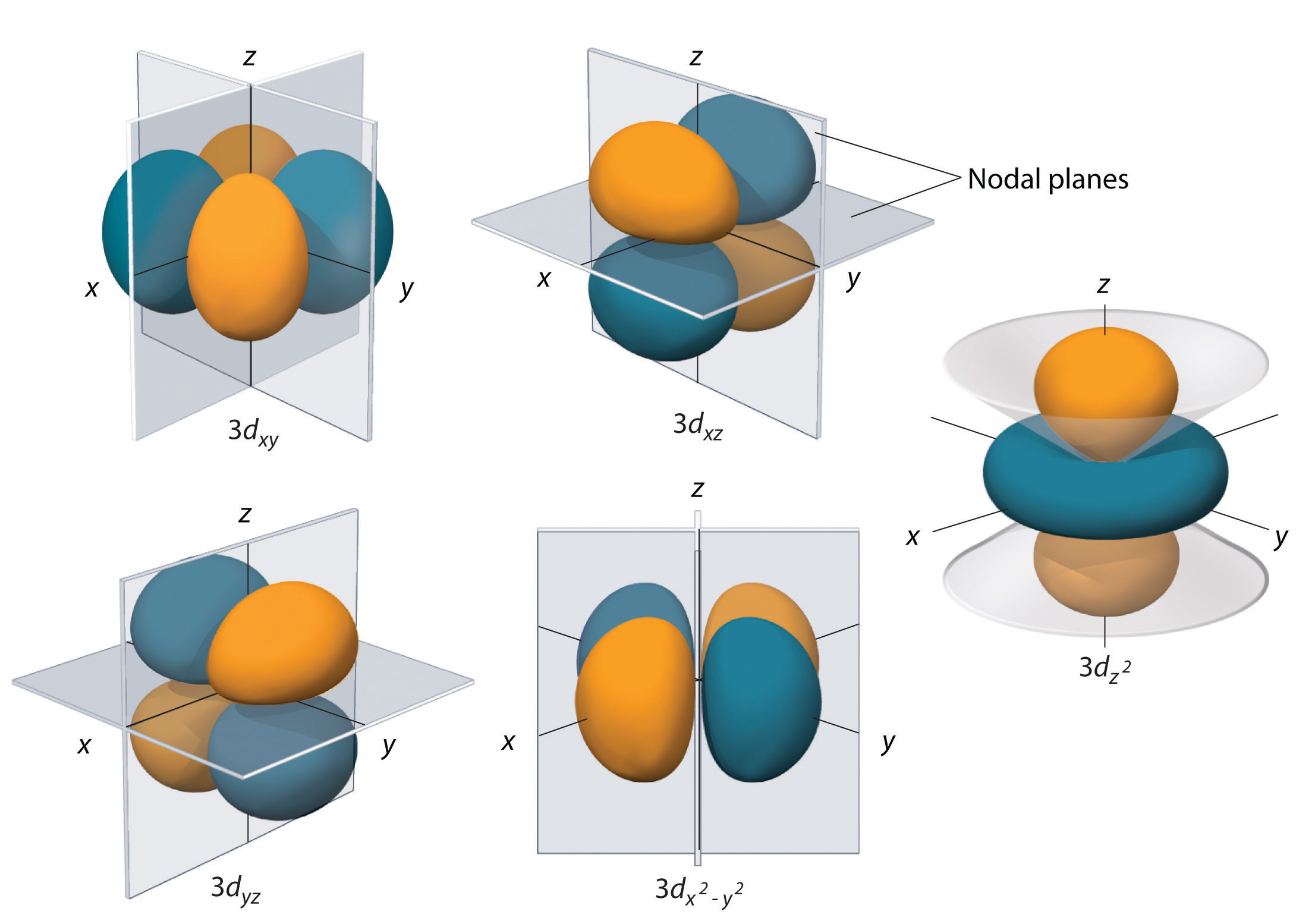
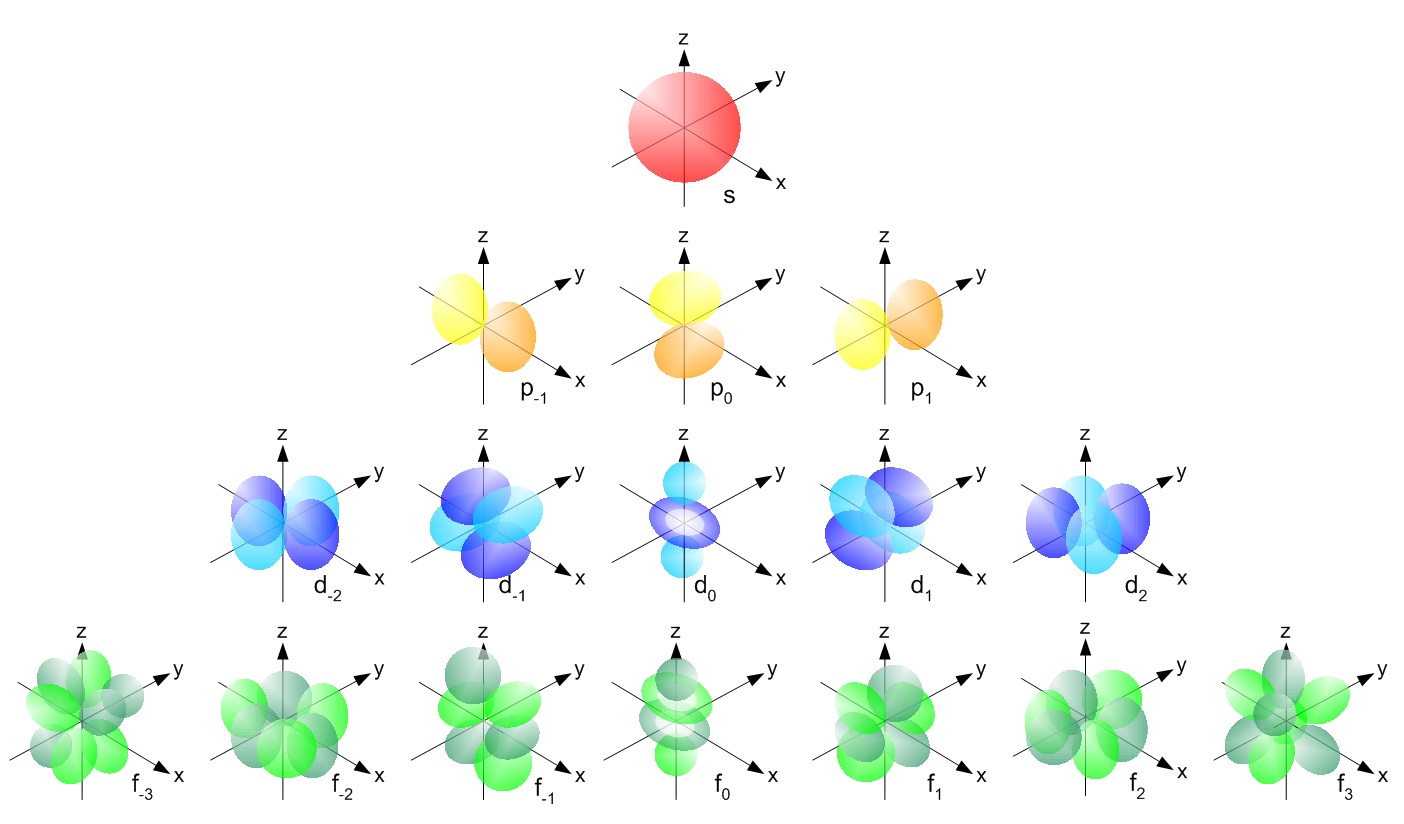
For d orbital Azimuthal quantum number l = 2 and the magnetic quantum number m = 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 Hence d orbitals have five orientations in space Thus d orbital corresponds to 4 double dumbbelled shapes (d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2 y 2) with the atomic nucleus at its centre and one dumb belled with dough nut shaped (d z 2) d orbital has twoThe "l" values tell you what suborbital an electron is found in You will see the lowercase letters s, p, d, f, g, and h for the suborbitals For example, the electron in a hydrogen (H) atom would have the values n=1 and l=0 The single electron would be found in the "K" shell and the "s" suborbitalThe number of possible values is the number of lobes (orbitals) there are in the s, p, d, and f subshells As shown in Table 1, the s subshell has one lobe, the p subshell has three lobes, the d subshell has five lobes, and the f subshell has seven lobes
Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding
What are s p d f orbitals
What are s p d f orbitals-All levels except the first have p orbitals d ORBITALS In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals which become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3px, 3py, 3pz)Here you will learn all about your basic ideas, techniques, termi



Clarifying Electron Configurations Chemical Education Xchange
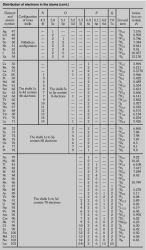
2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;(1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshell
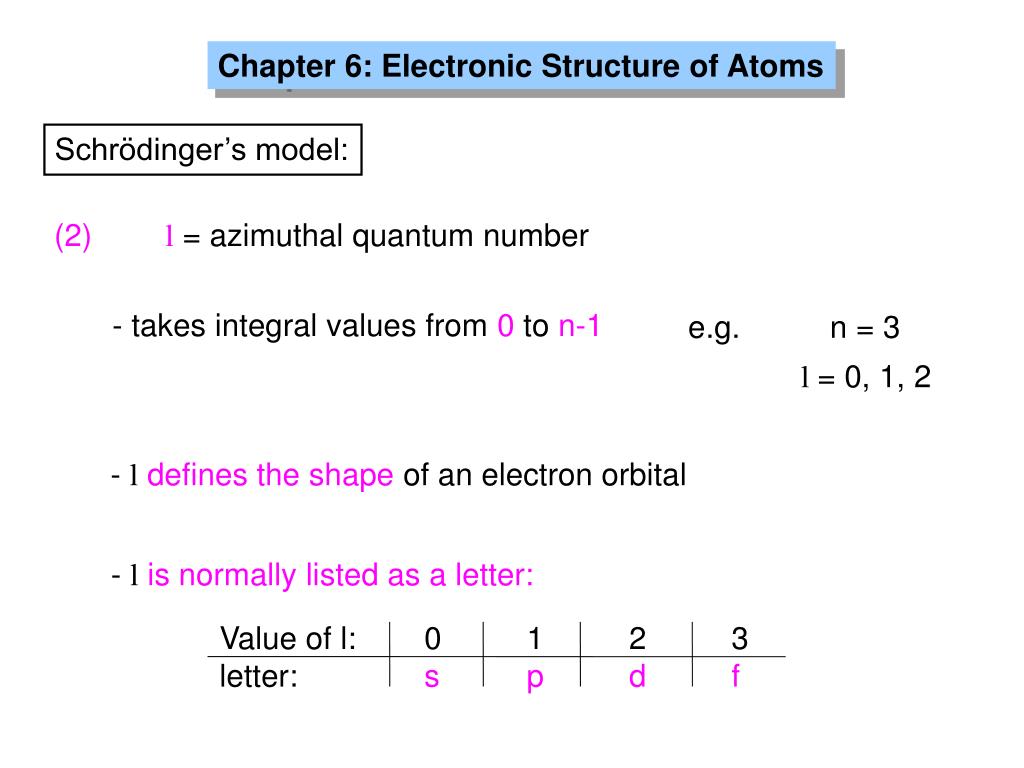
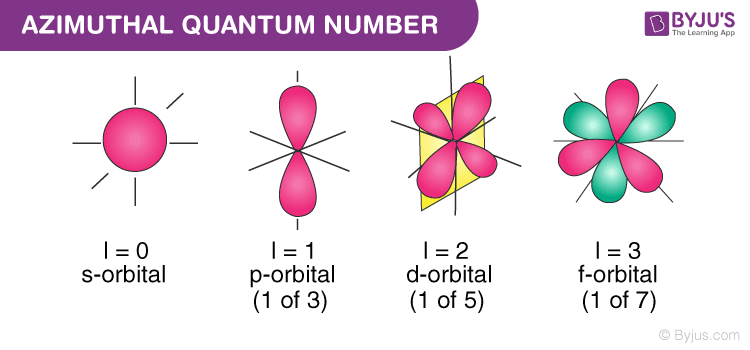
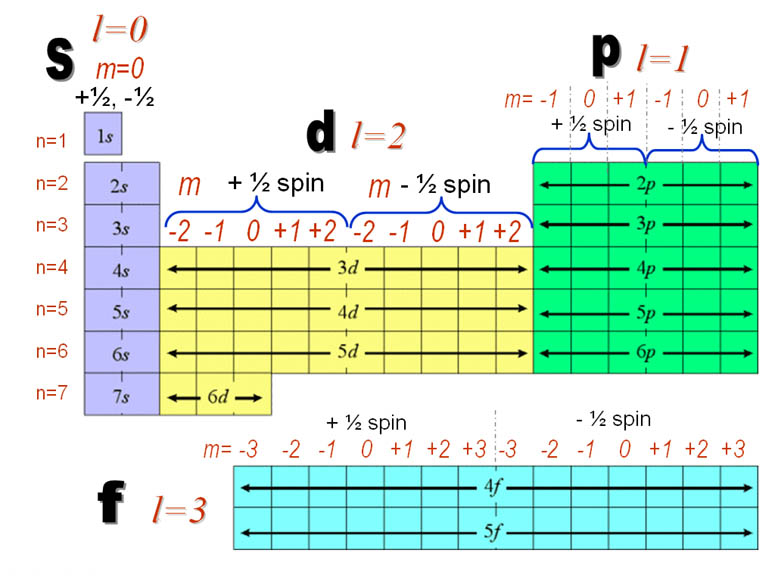
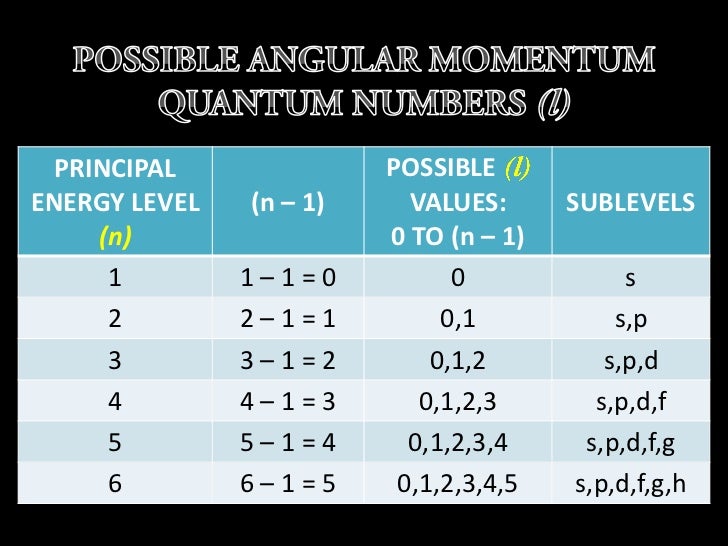
The energy of an electron is mainly determined by the values of the principal and orbital quantum numbers The principal quantum number is simply expressed by giving that number, but the orbital quantum number is denoted by a letter These letters, which are derived from the early days of spectroscopy, are s, p, d and f, which signify that the orbital quantum numbers l are 0, 1, 2 and 3How Orbitals are oriented in space?shapes of s, p, d and f orbitals Orbitals In spaceHi!There is one orbital in an s subshell (l = 0), three orbitals in a p subshell (l = 1), and five orbitals in a d subshell (l = 2) The number of orbitals in a subshell is therefore 2( l ) 1 Before we can use these orbitals we need to know the number of electrons that can occupy an orbital and how they can be distinguished from one another
Sublevels are commonly given letter designations The l = 0,1,2,3,4,5, sublevels are designated as s, p, d, f, g, sublevels, respectively For known elements no value of l higher than 3 (f sublevel) is necessary Two quantum numbers (n and l) are required to specify a particular energy sublevel The magnetic quantum number, m lThere is one orbital in an s subshell (l = 0), three orbitals in a p subshell (l = 1), and five orbitals in a d subshell (l = 2) The number of orbitals in a subshell is therefore 2( l ) 1 Before we can use these orbitals we need to know the number of electrons that can occupy an orbital and how they can be distinguished from one anotherThis number divides the subshell into individual orbitals which hold the electrons;


2 2 Atomic Orbitals And Quantum Numbers Chemistry Libretexts


3
Shape of the s, p, d, and f orbitalsChemistry Lecture #26For a pdf transcript of this lecture, go to wwwrichardlouiecom2 How many different orientations are there for S orbitals?Quantum numbers l = 2 and m = 0 represent d z 2 orbital Note For s,p,d and f orbitals, the value of the azmithual quantum number 'l' is 0,1,2,3 When l = 2, m can have values − 2, − 1, 0, 1, 2 A dsubshell can have five different orientations and orbitals corresponding to these orientations are d x y , d x z , d y z , d x 2 − y 2 d


Orbits And Orbitals Klm Vs Spdf Ppt Video Online Download



Quantum Numbers Video Quantum Physics Khan Academy
In quantum chemistry Ψ 2 provides us with the electron density it defines the size and shapes of the familiar orbitals s, p, d, f, etc Figure 2 sin 2 x vs x The diagram above shows sin 2 x has identical nodes to sin x;The orbitals rest along the x, y and z axis depending on the value of ml The 3 p orbitals will hold a total of 6 electrons d and f orbitals The third and higher shells have d orbitals which distinguish themselves from the previous orbitals by having two different shapes Four of the five orbitals are shaped like cloverleafs, each having fourBy signing up, you'll get thousands of


Spdf Orbitals Can Hold How Many Electrons Qecs Bamagien Site



File Atomic Orbitals Spdf M Eigenstates Mpositive Png Wikimedia Commons
1 S, P, and D Which are the sublevels in an energy level of n=4 S, P, D, and F How many electrons can S orbital hold 2 How many electrons can P orbital hold 6Thus, s, p, d, and f subshells are found in the n = 4 shell of an atom For l = 0 (the s subshell), m l can only be 0 Thus, there is only one 4s orbital For l = 1 (ptype orbitals), m can have values of –1, 0, 1, so we find three 4p orbitalsS p d f



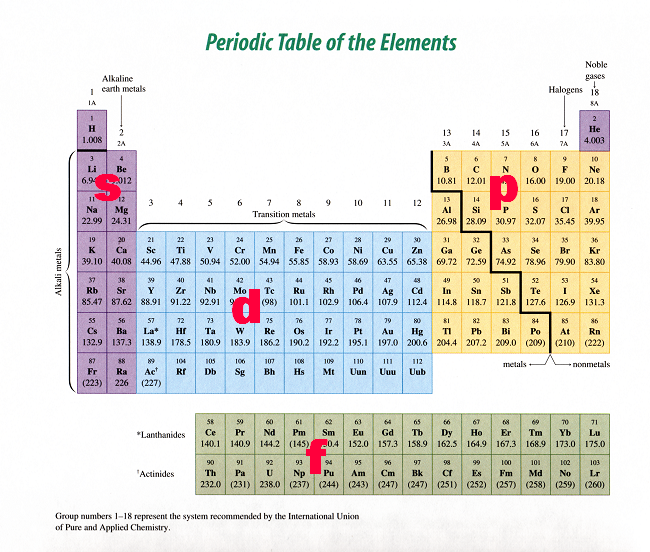
Periodic Table Blocks Of Elements



Magnetic Quantum Number Chemistrygod
For d orbital Azimuthal quantum number l = 2 and the magnetic quantum number m = 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 Hence d orbitals have five orientations in space Thus d orbital corresponds to 4 double dumbbelled shapes (d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2 y 2) with the atomic nucleus at its centre and one dumb belled with dough nut shaped (d z 2) d orbital has twoThe porbitals of higher energy levels have similar shapes although their size are bigger Shape of dorbitals For dsubshell, l = 2, there are five values of m namely 2, 1, 0, 1, 2 It means d orbitals can have five orientations These are represented by d xy, d yz, d zx, d x 2y 2 and d z 2;These orbitals are similar to the p orbital shape, but with more 'petals' like a cloverleaf They can also have ring shapes around the base of the petals The next orbital, ℓ=3 is called an f orbital These orbitals tend to look similar to d orbitals, but with even more 'petals' Higher values of ℓ have names that follow in alphabetical order



Angular Momentum Quantum Number Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
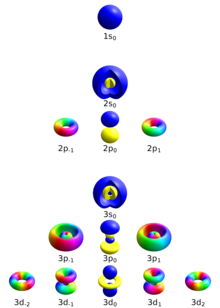


Quantum Number Wikipedia
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f s can hold 2 electrons p can hold 6 electrons d can hold 10 electrons f can hold 14 electrons Note that individual orbitals hold a maximum of two electrons There can be two electrons within an s orbital, p orbital, or d orbitalEach value for the angular momentum quantum number will correspond specifically with s,p,d, or f orbitals, which each have their own distinct shapes Which of the following quantum numbers can only take on values of 12 or −12?The rest being named in alphabetical order from G onwards, except that J is omittedWhen used to describe electron states in an atom, the term symbol usually follows the electron configuration



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange



File Atomic Orbitals Spdf M Eigenstates Png Wikimedia Commons
Orbitals Chemistry (s, p, d, and f Orbital) Atomic Orbitals are of four different kinds, denoted s, p, d, and f, each with a different shape Of the four, we'll be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry Learn more about atomic orbital at ByjusHow many possible values are there for the spin quantum number?The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3 respectively These names, together with the value of n , are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms


Energies Of Orbitals Concepts Factors Observations Videos Examples
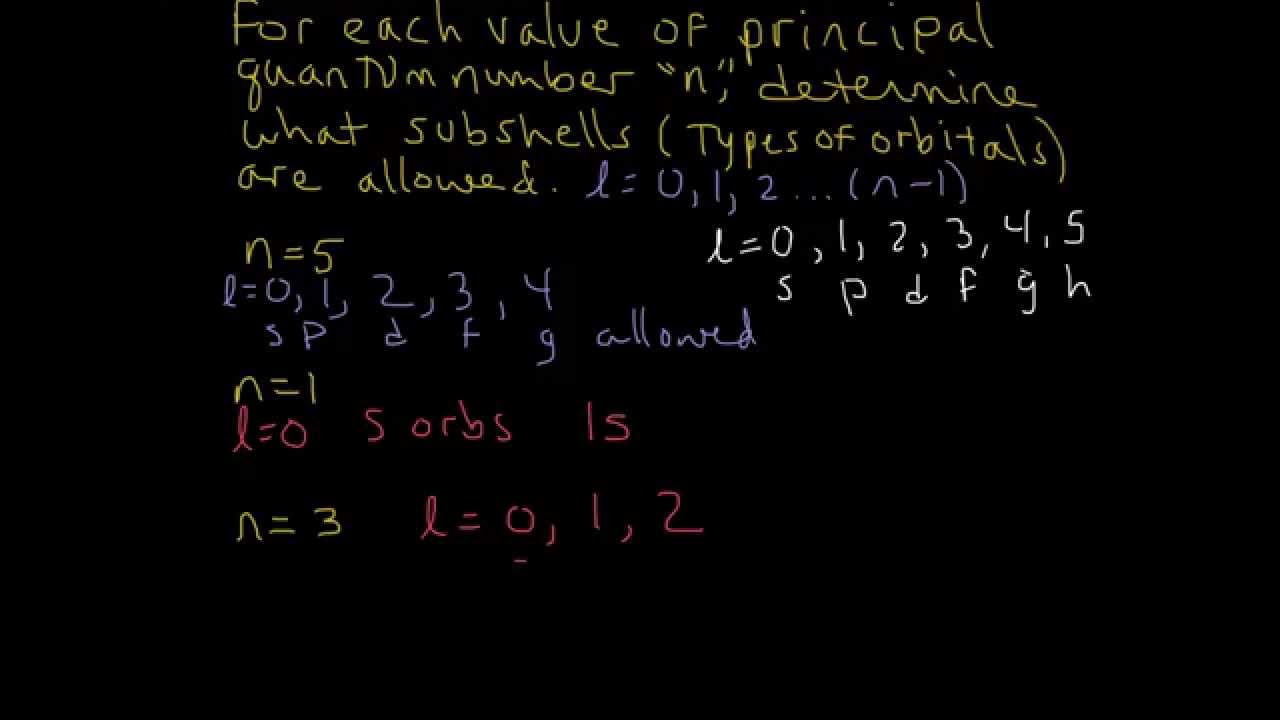


Quantum Numbers Example Determine Allowed Subshells S P D F Youtube
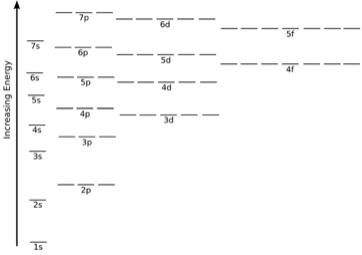
These are designated as p orbitals and have dumbbell shapes Each of the p orbitals has a different orientation in threedimensional space d Orbitals When l = 2, m 1 values can be −2, −1, 0, 1, 2 for a total of five d orbitals Note that all five of the orbitals have specific threedimensional orientations f OrbitalsThe number of angular nodes is equal to the value of the angular momentum quantum number \(l\) (For more information about angular nodes, see Electronic Orbitals) Each value of \(l\) indicates a specific s, p, d, f subshell (each unique in shape) The value of \(l\) is dependent on the principal quantum number \(n\)For the same value of n, the differences between the energies of s and p subshell are small whereas, between p and d subshell, it is large and so on With the increase in the value of n, the subshell of the lower shell may have higher energy than that of a higher shell which means 3d has higher energy than 4s


Ppt Chapter 6 Electronic Structure Of Atoms Powerpoint Presentation Id



Atomic Orbitals 5 1 Continued Tutorial Sophia Learning
S, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;The orbital shells are giving the names s,p,d,f base on the Spectroscopic transitions involving energy levels with different angular momentun (L) values with different groups of lines in the line spectra of the alkali metals The line groups were called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental s sharp for L=0 p principal for L=1A s orbital _ 2__ b the subshell of p orbitals __ 6___ c the subshell of d orbitals _ 10 __ d the subshell of f orbitals__ 14 __ e the subshell of g orbitals__ 18 __ 10
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



S P D F Block Chemistry Midterm 1 Flashcards Quizlet
The sublevel of p orbitalsThe sub level of D orbitalsThe sub level of F orbitals Place the following orbitals in order of increasing energy 1s, 3s, 4s, 6s, 3d, 4f, 3p, 7s, 5d, 5p The ml values for a d orbital are2, 1, 0, 1, 2 The allowed values of l for the level with n=2 are 0, 1How Orbitals are oriented in space?shapes of s, p, d and f orbitals Orbitals In spaceHi!The magnetic quantum number distinguishes the orbitals available within a subshell, and is used to calculate the azimuthal component of the orientation of orbital in space Electrons in a particular subshell (such as s, p, d, or f) are defined by values of ℓ (0, 1, 2, or 3) The value of m l can range from ℓ to ℓ, including zero


Q Tbn And9gcqvzit2fudmmakcvebiaidkonzjlqhjar5epxrmhawsxa 14hpo Usqp Cau


18 Electron Cloud Models
Footnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshellReview Question List the four orbital shapes The orbital shapes are s, p, d, and f Summarize Aufbau's rule for filling orbitals Electrons fill orbitals with theFootnotes (1) Each subshell is made up of a set of orbitals, the orbitals reflect which subshell they belong to by using the same letter, that is, there are s orbitals, p orbitals, d orbitals and f orbitals However, although there is only one s orbital in the s subshell, there are 3 p orbitals in the p subshell, 5 d orbitals in the d subshell, and 7 f orbitals in the 5 subshell



150 Quantum Numbers Ideas In 21 Chemistry High School Chemistry Teaching Chemistry


Q Tbn And9gctmvkgprvn1g6zt1zliwkaigfpfjmzuui8x0ol Ltjojmg4ziwl Usqp Cau
There are thus (2l 1) values of m l for each l value, ie one s orbital (l = 0), three p orbitals (l = 1), five d orbitals (l = 2), etc There is a fourth quantum number, m s, that identifies the orientation of the spin of one electron relative to those of other electrons in the systemThe "l" values tell you what suborbital an electron is found in You will see the lowercase letters s, p, d, f, g, and h for the suborbitals For example, the electron in a hydrogen (H) atom would have the values n=1 and l=0 The single electron would be found in the "K" shell and the "s" suborbitalF – orbital For f orbital Azimuthal quantum number l = 3 and the magnetic quantum number m =


Apchemistryatgwhs


Http Tinabatrascience Weebly Com Uploads 2 5 4 1 Quantum Number Practice Worksheet Key Pdf
F ORBITALS At the fourth and higher levels, there are seven f orbitals in addition to the 4s, 4p, and 4d orbitals Counting the 4s, 4p, and 4d orbitals, this makes a total of 16 orbitals in the fourth level They have even more complicated shapes s, p, d, and f orbitals are available at all higher energy levels as wellTo the s, p, d, f in order of increasing energy Each ℓ is a different orbital shape or orbital type This quantum number has integral values from 0 up to n1 Magnetic quantum number (mℓ) 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, Specifies which orbital within a sublevel you are likely to find the electron It determines the orientation of the orbitalEach value for the angular momentum quantum number will correspond specifically with s,p,d, or f orbitals, which each have their own distinct shapes Which of the following quantum numbers can only take on values of 12 or −12?



Atomic Orbital Chemistrygod



Quantum Numbers And Schrodinger S Wave Equation Chemistrybytes Com
Examples Electronic spectra The Laporte rule is a selection rule formally stated as follows In a centrosymmetric environment, transitions between like atomic orbitals such as ss, pp, dd, or ff, transitions are forbidden The Laporte rule (law) applies to electric dipole transitions, so the operator has u symmetry (meaning ungerade, odd) p orbitals also have u symmetry, so the symmetryFor example, 3d xy, 3d yz, 3d zx, 3d x 2y 2The magnetic quantum number distinguishes the orbitals available within a subshell, and is used to calculate the azimuthal component of the orientation of orbital in space Electrons in a particular subshell (such as s, p, d, or f) are defined by values of ℓ (0, 1, 2, or 3) The value of m l can range from ℓ to ℓ, including zero



Quantum Numbers And Schrodinger S Wave Equation Chemistrybytes Com


Electronic Configuration Article About Electronic Configuration By The Free Dictionary
To the s, p, d, f in order of increasing energy Each ℓ is a different orbital shape or orbital type This quantum number has integral values from 0 up to n1 Magnetic quantum number (mℓ) 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, Specifies which orbital within a sublevel you are likely to find the electron It determines the orientation of the orbitalReview Question List the four orbital shapes The orbital shapes are s, p, d, and f Summarize Aufbau's rule for filling orbitals Electrons fill orbitals with theThe nomenclature (S, P, D, F) is derived from the characteristics of the spectroscopic lines corresponding to (s, p, d, f) orbitals sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental;



A Would You Expect That Each Orbital Type S P D F Would Still Hold The Same Course Hero



Clarifying Electron Configurations Chemical Education Xchange
2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,Solved What are the possible m_1 values for each of the following types of orbitals s, p, d, and f?There are 2l1 orbitals in each subshell Thus the s subshell has only one orbital, the p subshell has three orbitals, and so on Spin Quantum Number (m s) m s = ½ or ½ Specifies the orientation of the spin axis of an electron



Using S P D Notations Describe The Orbital With The Following Quantum Numbers A N 1 L 0 B N 3 L 1 C N 4 L 2 D N 4 L 3


How Many Unpaired Electrons Are In A Copper Atom Socratic
The value of sin 2 x has no negative values ;Here you will learn all about your basic ideas, techniques, termi


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



Quantum Numbers N L Ml Ms Spdf Orbitals Youtube
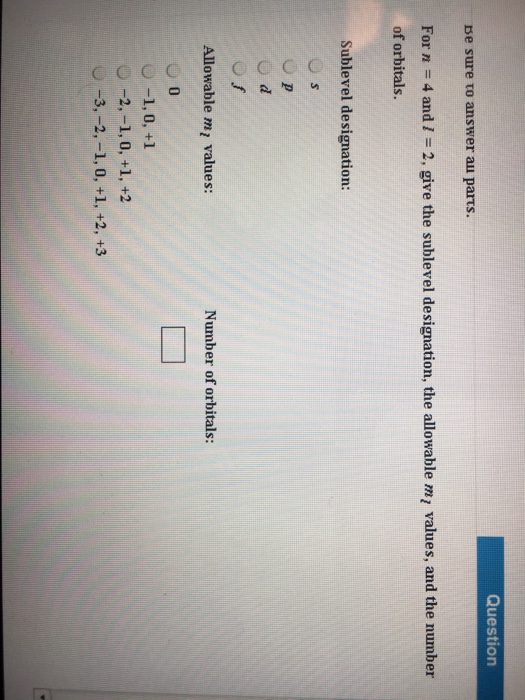


Solved For N 4 And L 2 Give The Sublevel Designation Chegg Com



Orbitals Chemistry For Non Majors



Electron Configuration Wikipedia



Quantum Numbers For The First Four Shells Video Khan Academy



Spdf Notation Definition In Music Kyzu Kilama Site



High School Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World



Chapter 7 Electron Configurations And The Properties Of Atoms 7 1
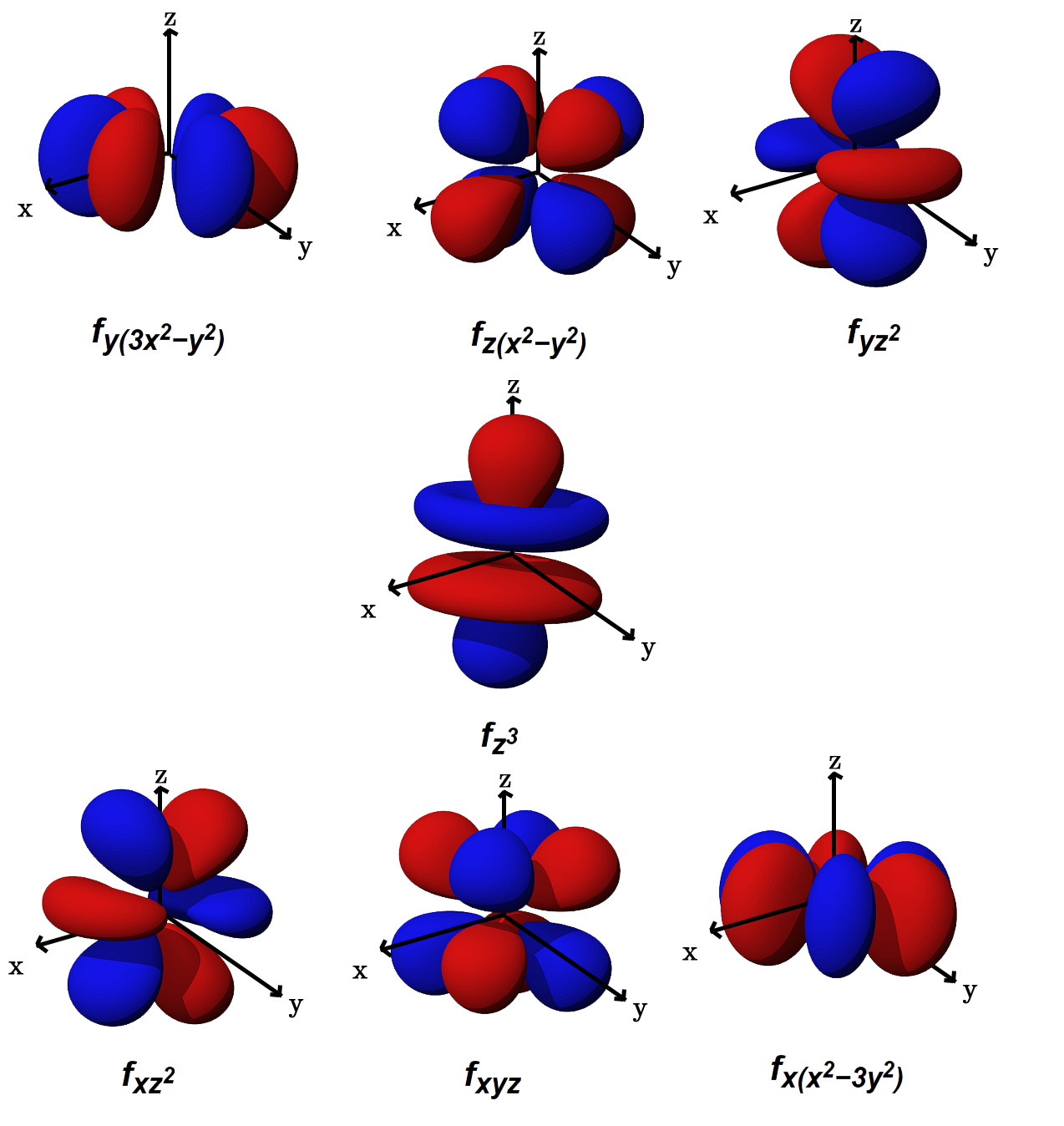


What Is The Shape Of F Orbital Example



Ground State Electron Configuration Definition Example Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry


How Many Electrons Can S P D F Orbitals Hold S Bravo Art Back Pain Doctor Delray Beach Utilities
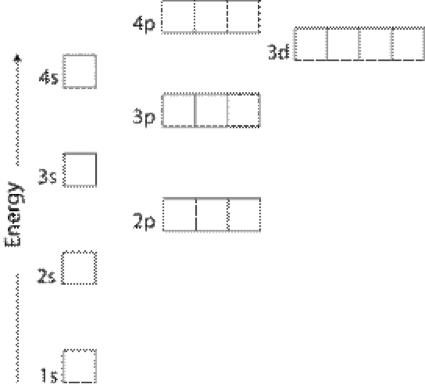


Electron Configurations Orbitals Energy Levels And Ionisation Energy Trends A Level Chemistry Revision Notes


Sublevel Spdf Chart Fgkb Katasekan Site


Organic Chemistry Atomic Structure Atoms And Atomic Orbitals Sparknotes



Chemistry 445 Lecture 3 Molecular Orbital Theory Ppt Download



Orbitals Chemistry For Non Majors


The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education


Chapter 2 5 Atomic Orbitals And Their Energies Chemistry Libretexts



Chemistry 1a Name Quantum Theory Periodic Trends 1 What Element Is Represented By The Electron Homeworklib


Quantum Numbers And Electronic Structure
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



Webelements Periodic Table Uranium Properties Of Free Atoms



S P D F Block Chemistry Midterm 1 Flashcards Quizlet


Azimuthal Quantum Number Definition Magnetic Quantum Number



Solved Please Help I Do Not Understand Atomic Orbitals A Chegg Com


Atomic Structure Atoms And Atomic Orbitals Sparknotes



Chem Chapter 8 Electron Configurations And Periodicity Studocu
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



Why Different Orbitals Have Different Shapes Britannica


Electron Shell Wikipedia


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


Quantum Numbers Are Just Like Address Of Electron In An Atom


Q Tbn And9gcrjaqjlb8lpy2zmnxb7djnungtx4z3mbsdjg7v7iofb5bmcmoq Usqp Cau


Periodic Table Ii Chemistry Gabriel Merces Brilliant


Www Philadelphia Edu Jo Academics Ajaber Uploads Ch 6 Quantum theory and the electronicstructure of atom Part3 Pdf


Quantum Mechanics


Chem4kids Com Atoms Orbitals



Chem105 Ch8 1 2nov Pdf Document


12 9 Orbital Shapes And Energies Chemistry Libretexts


Ch 9



Solved For N 3 And L 2 Give The Sublevel Designation Chegg Com


What Quantum Number Is Needed To Identify An Orbital In A Subshell How Are The Values Of This Quantum Number Controlled By Subshell Quora


Orbital Numbers For 21 Printable And Downloadable Gust



The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes


Http Employees Oneonta Edu Viningwj Chem111 Chapter07 Pdf



Shape Of The P1 2 Orbital Chemistry Stack Exchange


Pplato Flap Phys 8 3 Multi Electron Atoms


Difference Between Shell Subshell And Orbital Definition Structure Properties



Ch 6 Electronic Structure Of Atoms



Chemistry Electronic Structure Of Atoms Electron Configurations
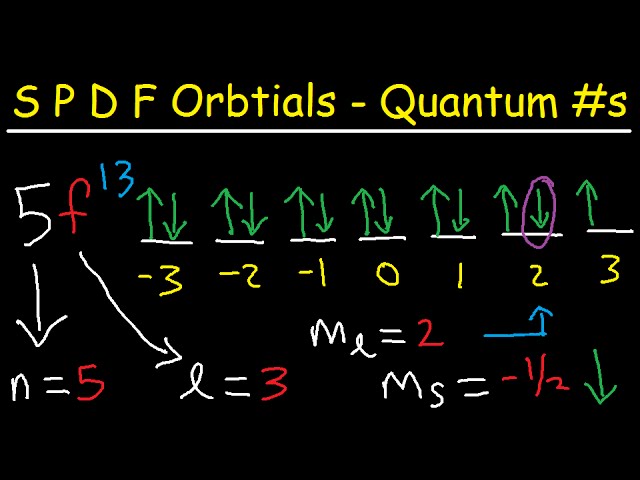


S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube



A An Atomic Orbital Has N 3 What Are The Possible Values Of L And M B List The Quantum Youtube


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes


Electron Configurations


Shapes Of Orbitals S P D Shapes
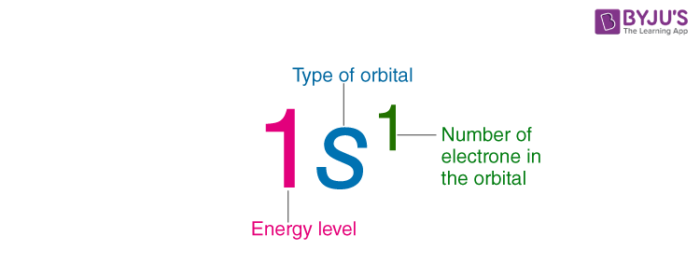


Electron Configuration Detailed Explanation With Examples
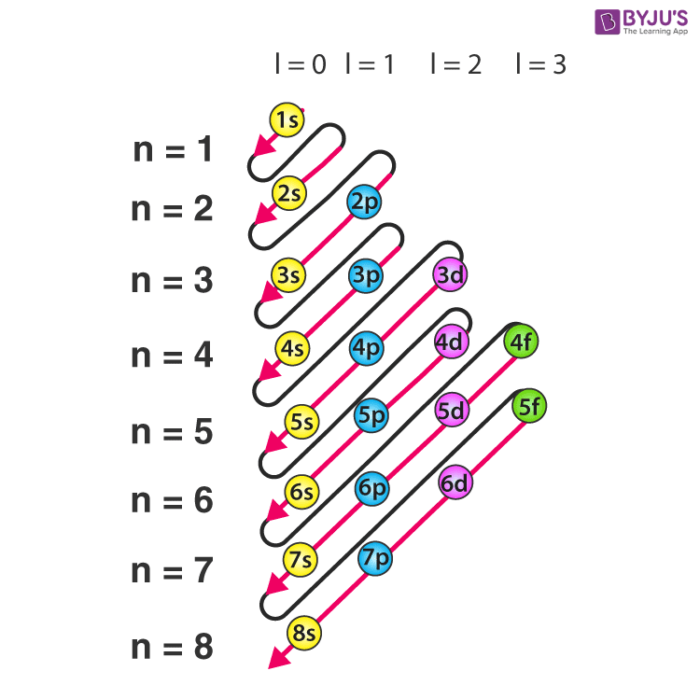


Electron Configuration Detailed Explanation With Examples


Www Philadelphia Edu Jo Academics Ajaber Uploads Ch 6 Quantum theory and the electronicstructure of atom Part3 Pdf


2


Electron Configurations



S P D F Orbitals Meaning Mypawl



S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



Periodic Table Spdf Block Dubai Khalifa



Quantum Mechanics N N The Principle Quantum Number Describes The Possible Energy Levels And Pictorially It Describes The Orbital Size N 1 2 3 Ppt Download



Ks9027 Set Of Seven F Orbital Models Klinger Educational Products



Electron Configurations And The Properties Of Atoms Flip Ebook Pages 1 50 Anyflip Anyflip



Chemical Orbitals From Eigenstates Poetry In Physics
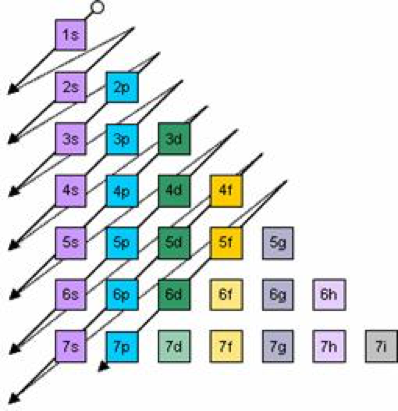


Electron Configurations Orbitals Energy Levels And Ionisation Energy Trends A Level Chemistry Revision Notes


How Were The Shapes Of S P D And F Orbitals Determined How Did They Get Their Names Of S P D And F Socratic


コメント
コメントを投稿